Technical Information Contact Us @ +91-9891-555-999
Technical Information
One of the key components of a tensile membrane /fabric structure is the tensile fabric. The kind of Fabric material you select will depend on your steel structure-design, durability, aesthetic appeal , Budjet and location requirements for the application.
Using exceptional quality tensile fabric materials we are able to create Tensile membrane structures and forms that were not possible earlier.
Commonly known as tensile fabric structures, these products are also referred to as tensile membrane roofs, tension membrane structures, architectural membrane structures, shell structures , Spatial Structures and fabric structures etc. In a laymen 's terms , sometimes also referred to as a Awnings.
Tensile Fabric Structures
A tensile fabric structure is a membrane (fabric) maintained under pre-stress (tension) state by structural elements and supporting systems.
Advantages of Tensile Fabric Structures
There are two shapes evident in tension fabric structures
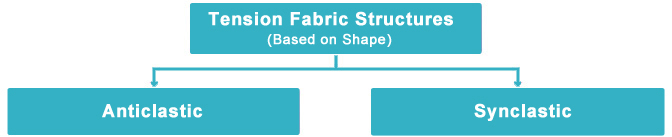
Anticlastic Structures
Anticlastic structures are pure tensile fabric surfaces having a curvature at a given point and in a particular direction, which is of the opposite sign to the curvature at that point in a perpendicular direction.
These are available in many free tension fabric forms and shapes such as:
Cones
Tensile membrane systems are somewhat unique in that they require minimal maintenance when compared to an equivalent-sized conventional building.
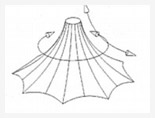
Arched Vault
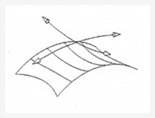
Parallel arches and crossed arches.
Hypar
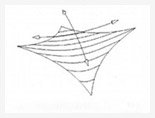
Two opposing high points and two opposing low points.
Synclastic Structures
Synclastic Membrane structures are air-supported surfaces having a curvature at a given point and in a particular direction that is of the same sign as the curvature at that point in the perpendicular direction.
For such air-supported structures, the fabric envelope is supported by pressurized air but most of the fabrics derive their strength from their double curved shape.
Two types of Tensile Fabrics are used in Tension Fabric Structures
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
On the basis of mechanical properties, weight and strength the International Convection has differentiated four distinct grades of fabrics. After the shape analysis, a project engineer decides the grade of fabric to used.
- PVC has been widely used for fabric structures for over twenty years.
- The fabric is translucent and the addition of white pigments increases its resistance to UV rays.
- Additives like anti fungal treatment, UV reflector and absorber agents are used to enhance PVC properties.
- For improving its durability, an extra coat of pigmented coating can be added.
- Flexibility can be improved by adding plasticizers (these might eventually drift to the surface attracting dirt and turning the PVC brittle, discolored and hard).
- PVC is welded by using high frequency welders.
The coating on the PVC is of utmost importance. A smooth and shiny coating facilitates to keep the fabric clean, it therefore essential to select the most appropriate fabric type during fabrication and installation.
PVC Fabrics are Classified into Several types Depending upon their Surface Coating
Acrylic lacquer coating is suited for marquee type colored structures that are cleaned regularly, reducing the chances of the structure getting dirty or damaged. This type of coating does not provide very high resistance to UV rays. An acrylic lacquer coating has 3-5 years warranty.
Polyvinyl DeneFlouride (PVDF) coating is widely used due to its durable nature. It sheds dirt easily and has a higher resistance to UV rays. One of its major drawback is that is not weldable in its pure form. To overcome this, many manufacturers dilute the PVDF with PVC to create an excellent quality, durable finish that needs no special preparation for welding. A PVDF coating has 7-12 years warranty depending upon the structure type and fabric.
Most of the fabric structures are faced with the wicking problem, i.e. water seeping the length of the thread lines of the fabric. This leads to the discoloration of the fabric and probable de lamination. To prevent this anti-wick polyester fiber is used.
Poly Tetra Fluoro Ethylene Coated Fibreglass (PTFE)
Another type of Tensile Fabric Structure is Poly Tetra Fluoro Ethylene Coated Fibreglass.- PTFE is chemically inert but bleaches white when exposed to sunlight
- It is unaffected by UV rays
- Has self cleaning properties making it virtually maintenance free
- Is fire resistant with a life span of over 25 years
- Limited colors, but specific shades can be custom made
- PTFE properties allow it to be fused and defused by the same instrument. This is very useful as damaged panels can be repaired on the site itself
- It has the second lowest co-efficient of friction amongst all the materials making it difficult to handle during manufacturing and installation phases
Difference between PVC and PTFE
| Attribute | PVC | PTFE |
| Durability | 10-15 years | Over 25 years |
| Chemical reactions | The fabric weakens on exposure to UV rays | Inert to almost all chemicals and solvents, but bleaches white when exposed to sunlight |
| Lighting requirements | The fabric is clear thus decreasing artificial lighting | As much as 25% translucency providing interior diffused light |
| Fire rating* | Moderate | Higher |
| Cost** | Moderate | At least five times more than PVC |
*How fire resistant a material is depends on the base fabric and the kind of coating on it. All the membrane materials will melt under high temperatures but the degree will vary.
**The cost of the fabric is a very small component of the overall project cost. The choice of fabric might not significantly alter the overall project cost.
Similarities between PVC and PTFE
- Extremely superior quality
- Excellent materials
- Can disperse light and create shade
- Waterproof
- Can span huge distances unsupported
- Have self cleaning properties
- Can block UV rays
